算法学习笔记第二讲
复杂度分析与基本数据类型:数组/链表/堆栈/队列
算法复杂度
Big O Notation,也称“大O复杂度”,分为:
- O(1): Constant Complexity: Constant 常数复杂度
- O(log n): Logarithmic Complexity: 对数复杂度
- O(n): Linear Complexity: 线性时间复杂度
- O(n2): N square Complexity 平方
- O(n3): N square Complexity 立方
- O(2n): Exponential Growth 指数
- O(n!): Factorial 阶乘
![[常见数据结构]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/1.jpg)
BigOCheatSheet复杂度:
![[来自BigOCheatsheet的复杂度分析]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/3.jpg)
根据主定理求解算法的复杂度:
![[根据主定理求解的算法复杂度]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/4.jpg)
Array
如下图所示,数组中所有元素在内存中连续存储:
![[数组内存示意图]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/5.jpg)
查找根据下标直接取值,插入和删除需连续移动后续元素,复杂度:
- Access: O(1)
- Insert: 平均 O(n)
- Delete: 平均 O(n)
LinkedList
![[链表示意图]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/6.jpg)
插入操作(cur之后,新节点new):
1 | |
删除操作(pre之后的cur节点):
1 | |
![[双链表]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/7.jpg)
复杂度:
- prepend: O(1)
- append: O(1)
- lookup: O(n)
- insert: O(1)
- delete: O(1)
实战题目:
-
- 思路:设定当前位置cur、前置指针pre,每次将cur的next指向pre,同时pre与cur后移 做这道题时先看了Python的解法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur=head,*pre=NULL,*next=NULL;
while(cur){
next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};这里一行进行了多次变量赋值,如果拆开是不行的,cur.next需要先用一个temp指针记录下来1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
cur,pre=head,None
while cur:
cur.next,pre,cur = pre,cur,cur.next
return pre
- 思路:设定当前位置cur、前置指针pre,每次将cur的next指向pre,同时pre与cur后移
-
- 思路一:快慢指针,当链表中存在环,则一快一慢两指针必定会相遇
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(!head || !head->next){
return false;
}
ListNode *fast=head,*slow=head;
while(slow && fast && fast->next){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}; - 思路二:集合判重。维护一个“经过集合”,每到一个节点,将节点加入集合。如果集合中已经存在该节点,则说明存在环。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11var detectCycle = function(head) {
let seen=new Set();
while(head!=null){
if(seen.has(head)){
return true
}
seen.add(head);
head=head.next;
}
return false;
};
- 思路一:快慢指针,当链表中存在环,则一快一慢两指针必定会相遇
-
- 思路:备份链表头,设置元素对的前指针pre、中间指针cur和后指针next,每次分别修改pre指针指向next,next指向cur,cur指向原next的next,pre后移到cur(不会重复 交换)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* fakeHead = new ListNode(0);
fakeHead->next = head;
ListNode* pre = fakeHead;
ListNode* cur=NULL ,*next=NULL;
while (pre->next && pre->next->next) {
cur = pre->next;
next = cur->next;
pre->next = next;
cur->next = next->next;
next->next = cur;
pre = cur;
}
return fakeHead->next;
}
};
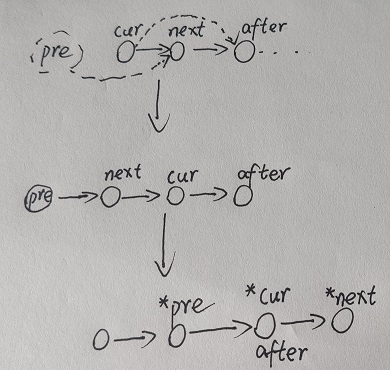
示意图:
- 思路:备份链表头,设置元素对的前指针pre、中间指针cur和后指针next,每次分别修改pre指针指向next,next指向cur,cur指向原next的next,pre后移到cur(不会重复 交换)
升级链表环,在检测链表环的基础上返回第一个进入环的节点。
- 思路:集合判重的方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11var detectCycle = function(head) {
let seen=new Set();
while(head!=null){
if(seen.has(head)){
return head
}
seen.add(head);
head=head.next;
}
return null;
};
- 思路:集合判重的方式
-
- 思路:顾名思义,以k为组,反转子链,再把子链接起来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43var reverseKGroup = function(head, k) {
const hair = new ListNode(0);
hair.next = head;
fakehead=head
let pre = hair;
let len=0
while(fakehead){
fakehead=fakehead.next;
len++;
}
while (head) {
if(len<k) return hair.next // 查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于 k
let tail = pre;
for(let i=0;i<k;i++){//提取子串
tail=tail.next
}
const nex = tail.next;
[head, tail] = reverse(head, tail);
// 反转子链接入主链
pre.next = head;
tail.next = nex;
pre = tail;
head = tail.next;
len-=k
}
return hair.next;
};
const reverse=(head,tail)=>{
let pre = tail.next;
let p = head;
while (pre !== tail) {
const nex = p.next;
p.next = pre;
pre = p;
p = nex;
}
return [tail, head];
}
- 思路:顾名思义,以k为组,反转子链,再把子链接起来
Stack
First In First Out (FIFO)
实现方式:Array or Linked List
push与pop两种操作:
![[push与pop]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/9.jpg)
Queue
First In Last Out (FILO)
实现方式:Array or Linked List
元素进出示意图:
![[元素进出]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/10.jpg)
![[复杂度]](/2022/08/10/algorithm-2/11.jpg)
实战题目
-
- 思路:栈的特点是先入后出,队列的特点是先入先出,若要用栈实现队列则可用两个栈“联动”的方式实现。
- 维护一个input栈和一个output栈
- 新增元素的时候,直接压入input栈
- 弹出元素的时候,先看output是否为空,不为空直接弹栈,若为空则将input栈全部弹入output,再在output弹出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> input,output;
int top;//临时全局变量栈顶元素
MyQueue() {}
void push(int x) {
input.push(x);
}
int pop() {
// 若output为空,则将input全部弹出并压入output中,然后output.pop(),后续push进入的还是要pop到output
if (output.empty()) {
while (!input.empty()) {
top=input.top();
output.push(top);
input.pop();
}
}
top=output.top();
output.pop();
return top;
}
int peek() {
// 若output为空,则将input全部弹出并压入output中,然后output.peek()
if (output.empty()) {
while (!input.empty()) {
top=input.top();
output.push(top);
input.pop();
}
}
return output.top();
}
bool empty() {
return output.empty() && input.empty();
}
}; - 思路:栈的特点是先入后出,队列的特点是先入先出,若要用栈实现队列则可用两个栈“联动”的方式实现。
用队列实现栈
思路:- 栈的特点是先入后出,队列是先入先出,若用队列实现栈,则需在元素入队后将元素逆置,让新元素维持在队列首,以前插入的在队列尾,这样出队的时候顺序就能反过来
- 可以用C++维护一个队列,新增元素入队时先入队,
c++版:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
int len,front;//辅助全局变量len:队列长度,front:队首元素
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {}
//压栈,需要根据栈长度,全部先弹出栈再压栈
void push(int x) {
len = que.size();
que.push(x);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
}
//通过front()获取元素,弹出直接pop即可
int pop() {
front = que.front();
que.pop();
return front;
}
//获取栈顶元素
int top() {
return que.front();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};JavaScript版:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20var arr=[]
var MyStack = function() {
arr=[]
};
MyStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
arr.push(x)
};
MyStack.prototype.pop = function() {
if(arr.lenth>=1){
return arr.pop()
}
};
MyStack.prototype.top = function() {
if(arr.length>=1){
return arr[arr.length-1]
}
};
MyStack.prototype.empty = function() {
return arr.length==0
};有效括号判断
左括号必须和右括号成对出现- 思路一:
- 出现左括号,不能判别是否出现不匹配,只能先暂存处理;
- 出现右括号,则必须看左边括号是否相符,若相符则左边相邻括号,继续判断后续字符
- 使用栈,左括号压栈,右括号弹栈,到了字符串末尾判断栈是否为空
- 复杂度分析:弹栈/压栈操作的复杂度为O(1),最坏情况每个字符串判断并操作一次,时间复杂度O(1),空间复杂度O(n) 这里一开始用的是map,后面改用unordered_map,前者是红黑树有序存放,后者基于哈希表无序排列,性能上更快。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
int len=s.length();
if(len%2==1) return false;
stack<char> closing;
unordered_map<char, int> charmap = {//一个字符映射,目的是查找与右括号对应的字符
{')','('},
{']','['},
{'}','{'}
};
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(s[i]=='('||s[i]=='{'||s[i]=='['){
closing.push(s[i]);
}
else if(closing.empty() || charmap.find(s[i])->second!=(closing.top())){
return false;
}
else{
closing.pop();
}
}
if(closing.empty()) return true;
return false;
}
};
- 思路二:
- 若括号能匹配,则字符串中必然有“()” “{}” “[]”等字符组合。
- 使用Java或JavaScript的replace函数,先将内层的、能直接匹配的括号对去掉
- 循环replace,将原来外围的括起来的括号对消去,当字符串长度不再变了停止循环,判断字符串是否为空
- 复杂度分析:最坏情况时间复杂度O(n2/2),空间复杂度O(1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int len;
do{
len=s.length();
if(len%2==1) return false;
s=s.replace("()","").replace("{}","").replace("[]","");
}while(len!=s.length());
return (s.length()==0);
}
}
- 思路一: